

Amides do undergo acyl substitution reactions in biochemical pathways, but these reactions are inherently slow and the enzymes catalyzing them have evolved efficient strategies to lower the activation energy barrier.Ĭarboxylic acids and esters are in the middle range of reactivity, while thioesters are somewhat more reactive. Lactones are important derivatives of carboxylic acids in both organic synthesis and in. Section 20 - Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions. generally an increase in resonance an increase in stability an decrease in reactivity. In amides, the nitrogen atom is a powerful electron donating group by resonance – recall that the carbon-nitrogen bond in peptides has substantial double-bond character – thus amides are relatively unreactive. The carboxylic acids, acid halides, and esters are reduced to alcohols, while the amide derivative is reduced to an amine. Fischer esterification can be used to make lactones (cyclic esters).
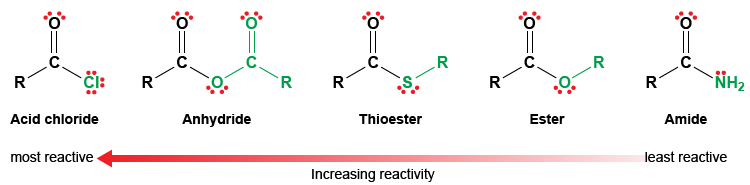
The negatively charged oxygen on the carboxylate group has lots of electron density to donate, thus the carbonyl carbon is not very electrophilic. This depends on how much electron density the neighboring heteroatom on the acyl X group is able to donate: greater electron donation by the heteroatom implies lower partial positive charge on the carbonyl carbon, which in turn implies lower electrophilicity. Here’s another way to think about the relative reactivites of the different carboxylic acid derivatives: consider the relative electrophilicity, or degree of partial positive charge, on the carbonyl carbon in each species. This is why it is not possible to directly convert an ester, for example, into a thioester by an acyl substitution reaction – this would be an uphill reaction. Relative Reactivity of Derivatives Anhydrides are most reactive since their resonance stability and three electron withdrawing oxygen atoms are the most.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
